

I’ll provide examples and resources to help you further your understanding of this Spanish grammar topic.
Take Note: According to the data collected by El Instituto de Verbología, almost 30% of the verbs we use daily are pronominal verbs (including reflexives).
Learning Spanish?
Join the Tell Me In Spanish community and get a copy of my step-by-step Spanish Learner’s Roadmaps and tricky synonyms & vocab cheat sheets.
Reflexive verbs in Spanish are verbs that express a reflexive action. Simply, they refer to activities that the subject does upon oneself.
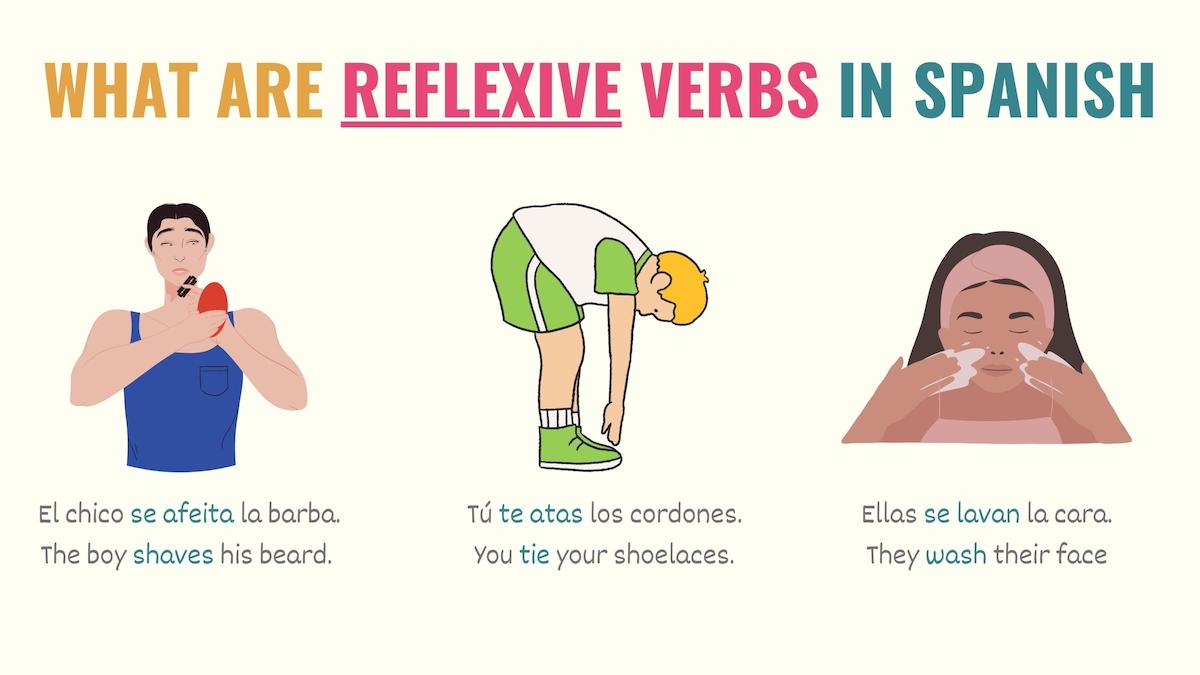
From a Spanish grammar point of view, with a reflexive verb, the subject and the object (the receiver of the action) are the same person. For example:
[Reflexive pronoun] + [verb conjugated]
Yo me cepillo los dientes.
I brush my teeth.
Ella se ducha con agua fría.
She showers with cold water.
Tú te afeitas todos los días.
You shave every day.
As you can see in the sentences above, the subjects are doing the actions upon themselves. You’re shaving, and the person you’re doing this to is yourself.
Take Note: Reflexive verbs in Spanish can be translated into English as ‘myself’, ‘yourself’, ‘himself’, ‘herself’, etc. However, it’s important to note that the translation of reflexive verbs in English may not always include reflexive pronouns.
A reflexive verb in Spanish requires an appropriate reflexive pronoun (me, te, se, nos, os) that matches the subject of the sentence.
Ellos se despiertan temprano.
They wake up early.
Nosotros nos lavamos las manos.
We wash our hands.
In their non-conjugated form (infinitives), reflexive verbs end with the pronoun se, such as bañarse, vestirse, and dormirse.

As established before, reflexive verbs in Spanish describe actions that the subject performs upon oneself. However, if the action is directed towards someone else, you must use non-reflexive verbs.
Check these sentences:
| Reflexive action | Non-reflexive action |
|---|---|
| Yo me cepillo el cabello. I brush my hair. | Yo le cepillo el cabello a la bebé. I brush the baby’s hair. |
| Connie se lavó las manos. Connie washed her hands. | Connie las lavó (las cortinas). Connie washed them (the curtains). |
When the action is directed to something or someone else, non-reflexive verbs in Spanish are combined with indirect and direct object pronouns.
Since the action falls back into different people, mixing these types of verbs can lead to misunderstandings. So, make sure you understand the difference between non-reflexive and reflexive verbs.
Take Note: Reflexive verbs in Spanish are transitive verbs. In other words, they need an object to be complete. Some non-reflexive verbs are also transitive, while others don’t require an object to have full meaning –yo trabajo.

Spanish reflexive verbs are usually associated with daily routines, hygiene, and grooming activities. Here are some examples of reflexive verbs:
Here are some sentences using these verbs:
No te abrochaste la camisa.
You didn’t button your shirt.
¿Ya os lavasteis las manos?
Did you guys already wash your hands?
Espérame, me voy a cambiar.
Wait, I am going to change.
¿Dónde nos podemos lavar las manos?
Where can we wash our hands?
Los niños no se han puesto la pijama.
The kids have not put on their pajamas.
In this list of most common reflexive verbs, you can check other verbs to add to your vocabulary.
Like any other Spanish verb, a reflexive verb must be conjugated. To do so, you must identify the conjugation group (-AR, -ER, -IR) and apply the appropriate endings. On top of following the standard conjugation rules, you must also use reflexive pronouns.
Here is table with the present tense conjugation of cepillarse, vestirse, and ponerse.
| -AR Verbs | -ER Verbs | -IR Verbs | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yo | Me cepillo | Me pongo | Me visto |
| Tú | Te cepillas | Te pones | Te vistes |
| Él / Ella / Usted | Se cepilla | Se pone | Se viste |
| Nosotros | Nos cepillamos | Nos ponemos | Nos vestimos |
| Vosotros | Os cepilláis | Os ponéis | Os vestís |
| Ellos / Ellas / Ustedes | Se cepillan | Se ponen | Se visten |
Putting the Spanish reflexive pronouns aside, the conjugation of reflexive verbs follows the same pattern as their non-reflexive forms. In other words, these verbs can also be irregular or have stem changes (like ponerse and vestirse).

In their infinitive form, reflexive verbs end with ‘se’ (bañarse, vestirse). When it comes to conjugating, this ‘se’ ending can be very confusing for Spanish learners. However, ‘se’ indicates that you’re dealing with a reflexive verb and it will need to be replaced by the proper reflexive pronoun.
Unlike personal pronouns, reflexive pronouns cannot be omitted because the sentence would lose its reflexive meaning.
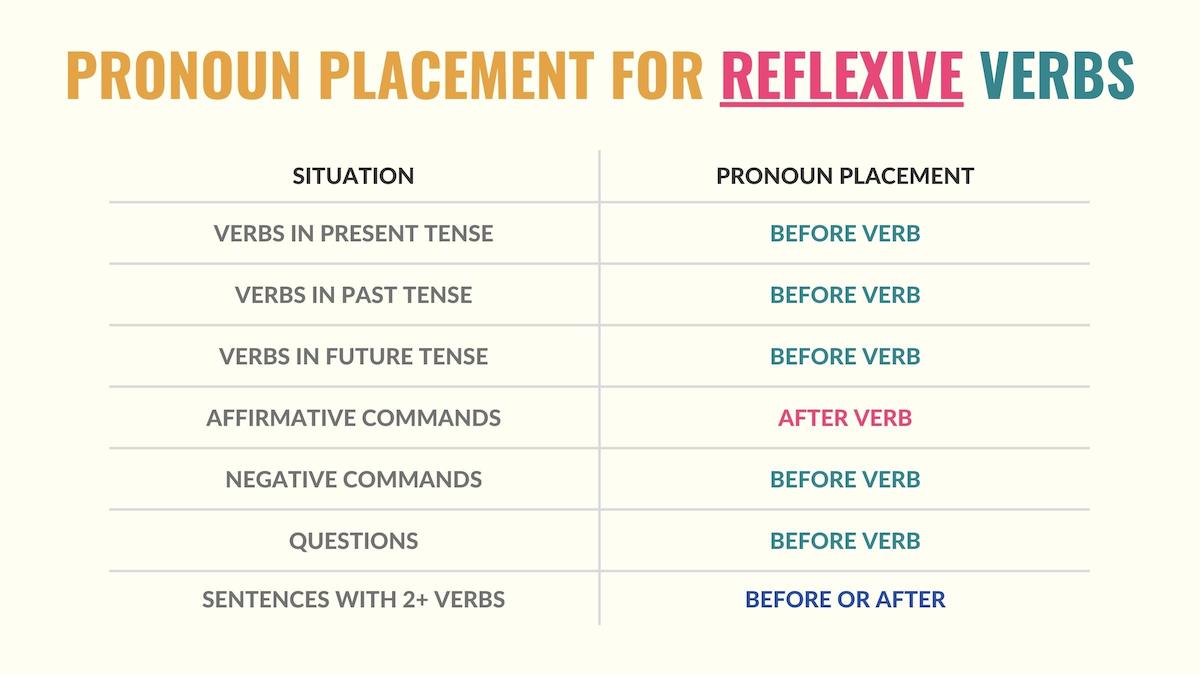
Also, keep in mind that the pronoun’s position can vary depending on the tense or mood. So, make sure you understand how to conjugate reflexive verbs in Spanish.
If you’re learning Spanish, you cannot overlook reflexive verbs. In fact, there are many actions you can’t express without them. Here are some key points and rules you should keep in mind:
Now that you know what a reflexive verb is in Spanish, some additional resources can help you master this topic.. First, understand how transitive verbs work. This will allow you to get familiar with verbs that take an object, such as reflexives and non-reflexives.
As mentioned above, if the action is done to a different object, you’ll need different object pronouns. So, make sure you get familiar with direct and indirect objects. If you’re still confused about the conjugation rules you must use, you should check this guide.
In fact, here are some examples you can use as guidelines:
On a final note, verbs using reflexive pronouns are called pronominals. Many pronominal verbs describe reflexive actions, but this may not always be the case.
Reflexive verbs can be a challenging subject for Spanish beginners to understand. If you found this guide useful, I’ve created a free PDF of the graphics, key points and cheat sheets. Since knowing how to use a verb in reflexive form is critical to becoming fluent, you can download a copy and revisit this topic whenever you need a refresher or are ready to level up your Spanish skills.
Here are some Spanish quizzes that can help you put this knowledge into practice: